
Case study: Modal Analysis of a L-0 Blade
Stage: Large L-0 steam turbine
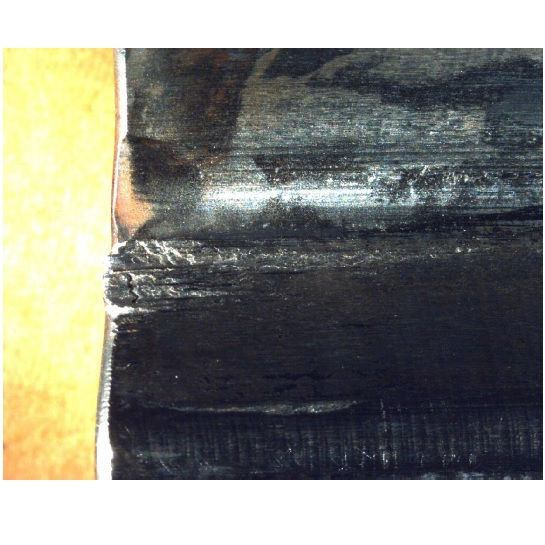
Issue: cracks occurred in the root of multiple blades after a relative short period of time in service
Objectives: Root cause analysis of cracking, interpretation of BVM data and evaluation of new blade design
Diagnosis: Cracking was attributed to high cycle fatigue (HCF) under broad band excitation
Solutions: Adopt OEM redesigned blade featured with additional damping elements and comply with the guidelines developed for BVM system





Background
-
Cracks were found in the root of multiple blades after a relative short period of time in service.
-
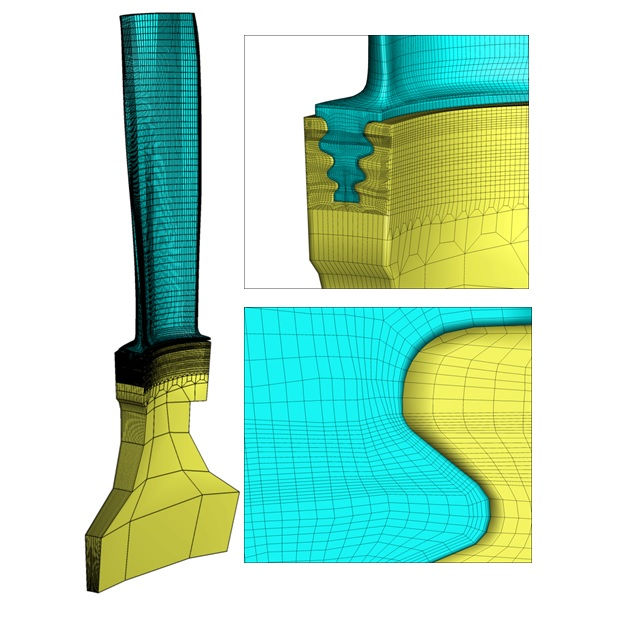
TTI was requested to undertake a design evaluation on both original freestanding and new damped L-0 blade proposed by OEM.
-
TTI was also tasked to verify the prescribed guideline by deriving the relationship between BVM tip displacements and dynamic stress at the crack sites.
Summary of Analyses
-
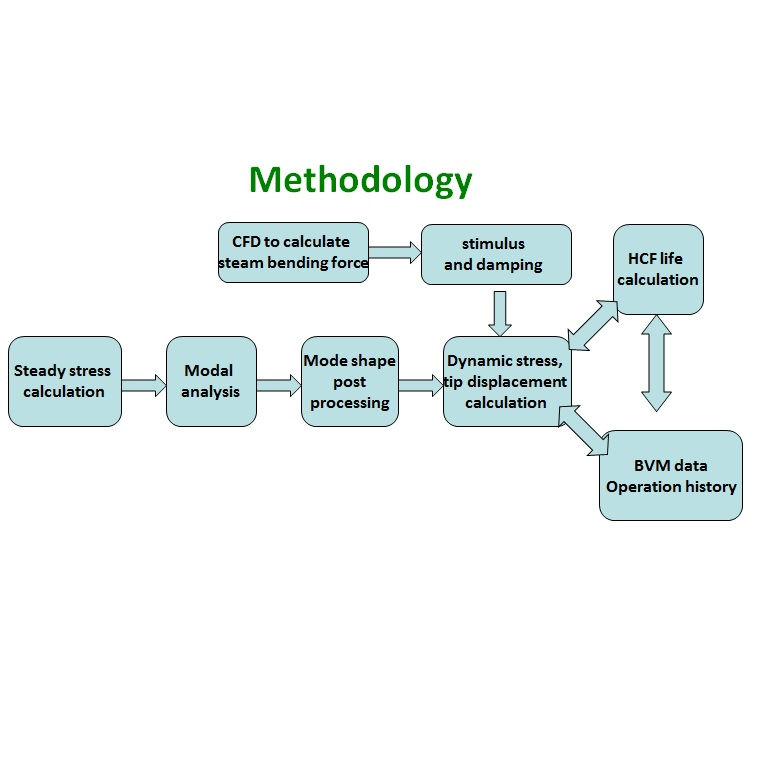
At-speed frequencies and mode shapes of the bladed-disk structure were calculated by FEA analysis. Results were used to correlate against BVM data and provide the basis to estimate actual dynamic stresses under non-synchronous vibration.
-
Critical locations with predicted peak dynamic stresses are consistent with field observation. Critical vibrating modes due to broad band excitation were identified.
-
A series of CFD simulations were conducted to assess the performance for both original and new blades under different load conditions.
-
Design of the new blade with introduction of the damping elements was evaluated and verified by analysis.

